J. Welles Wilder's Parabolic Stop and Reversal is a simple study to use. The study continuously computes "stop and reverse" price points. Whenever the market penetrates this "stop and reverse" point, you liquidate your current position and take the opposite position. If long, you liquidate the long position and establish a short position. If short, you liquidate the short position and establish a long position. The Parabolic Stop and Reversal study always has you in the market.
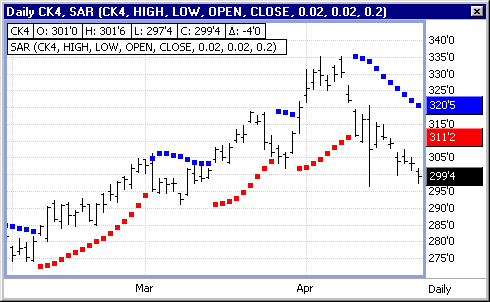
This example displays a daily chart with a plotted parabolic Stop and Reversal (SAR). The points where the indicator intersects a chart bar show the dots plotted on the opposite side of the chart bars. The SAR on top of the prices indicates a short position. When the SAR is below the prices, a long position should be established. (The colors of the short and long positions may be established in the study's properties.) The points where the parabolic SAR intersects a bar are the stop and reverse points or the SAR points.

While the calculations to derive the "stop and reverse" price are quite tedious, the concept of the study is a model of simplicity. If the trading adage, "The trend is your friend," has merit, this study is the mathematical expression of that adage. Once you initiate a position, the Parabolic Stop and Reversal study gives the market time to move in your favor. If the market does not move in your favor, you need to stop and reverse your position. This study always has a market position.
Wilder defines the "stop and reverse" price as the SAR. The value of the SAR is a function of both time and price. When you enter a position, either long or short, the SAR value moves slowly during the first few trading intervals. This allows the market to work in your favor. But as time progresses, the SAR is either hit, or it follows the market direction in your favor. Remember, the SAR price never reverses. It moves higher or lower with the market and always in the direction of your market position. It is an automatic trailing stop.
When the market trades or touches the SAR value, you stop and reverse your position. This study works best in a trending market. You can imagine the severe whiplash that develops in a choppy, sideways market. In fact, Wilder recommends using this study in conjunction with the Directional Movement Index. The DMI helps you to determine the predominant trend of the market, and it assists you in trading the market from that side only. For a complete discussion, please refer to Wilder's book, "New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems".
The Parabolic Stop and Reversal study uses two values in the computations. They are the Acceleration Factor, and the Acceleration Limit. Wilder used the values of .02 and .20, respectively.
Properties
InitialAccelerationFactor: The acceleration factor in 1/1000, or the SAR step size, which starts at 0.02 and increases by the AccelerationAdditionFactor with each step to a maximum of 0.20. For example, if the trade makes new highs for three consecutive days, then the SAR step increases by 0.02 every day (0.02 to 0.04 to 0.06, etc.) The application uses as default of .02 (2/1000 or .02).
AccelerationAdditionFactor: The SAR step size. The application uses as default of .02 (2/1000 or .02).
AccelerationFactorLimit: The maximum value the SAR step can reach. Welles Wilder recommends a maximum acceleration limit of 0.20 for most instruments. The application uses as default of .20 (200/1000 or .20).
Computing Parabolic Stop and Reversal
The computational procedure for the Parabolic Stop and Reversal study is a logic exercise. The actual computations are quite simple. The logic to derive those computations is somewhat more complex.
You must first determine the starting point for the calculations. The applet examines the first two trading intervals on the price chart within the active window. If the close for the second trading interval exceeds the close for the first trading interval, assume a long position. Conversely, if the closing price for the second trading interval is less than the close for the first trading interval, assume a short position. This is slightly different from Wilder's discussion, but it is the technique the applet uses to compute the study.
Once the market establishes a direction, the initial SAR becomes the extreme price (EP) for the two intervals. The extreme price is either the lowest price or highest price for the two trading intervals. The short position uses the high price, and the long position uses the low price.
Formula
Determine if initial-position (P) is long or short. FutureSource assumes a short position if the close of the initial-position is less than the prior close. If the inverse is true, FutureSource assumes a Long position. FutureSource's technique in determining the initial position differs slightly from Wilder's discussion.
Pi = Short if Ct < Ct-1
Pi = Long if Ct > Ct-1
Determine initial Stop and Reversal (SAR) - based on previous Low (L) or previous High (H) depending on current position.
If Pi = Short, then SARi = Ht-1
If Pi = Long, then SARi = Lt-1
Determine initial Extreme Price (EP)
If Pi = Short, then EPi = Min(Lt, Lt-1)
If Pi = Long, then EPi = Max(Ht, Ht-1)
Determine Acceleration Factor (AF) - Use "Y" for the initial AF, increasing the value by "Y" on each day that a new EP is made until a position ends. Do not increase the AF above "Z"
A. When PTt is a new position, AFt = Y (Acceleration Factor is reset to the initial value)
B. If EPt = EPt-1, then AFt = AFt-1 (High or Low does not change the EP, therefore AF does not change)
Calculate AFD (Acceleration Factor multiplied by the absolute value of the difference between EP and SAR)
AFDt = AFt * (ABS(EPt - SARt))
Determine subsequent values of Position, Extreme Price and Stop And Reversal:
A. If Pt-1 = Long, and if (SARt-1 + AFDt-1) > Lt then:
Pt changes to Short
EPt = Lt
SARt = EPt-1
B. If Pt-1 = Long, and if (SARt-1 + AFDt-1) < Lt then:
Pt remains Long
EPt = MAX(Ht, Ht-1 ... Ht-X)
SARt = MIN((SARt-1 + AFDt-1), Lt-1, Lt-2)
C. If Pt-1 = Short, and if (SARt-1 - AFDt-1) < Ht then:
Pt changes to Long
EPt = Ht
SARt = EPt-1
D. If Pt-1 = Short and If (SARt-1 - AFDt-1) > Ht then:
Pt remains Short
EPt = MIN(Lt-1, Lt-2, ... Lt-X)
SARt = MAX((SARt-1 - AFDt-1), Ht-1, Ht-2)
ABS = Absolute Value
AF = InitialAccelerationFactor
AFD = InitialAccelerationFactor multiplied by the absolute value of the difference between Extreme Price value and SAR value
C = Close Price
EP = Extreme Price (Maximum High or Minimum Low over a period, depending on Period type)
H = High Price
i =initial value (chronologically first calculated)
L = Low Price
MAX = Maximum
MIN = Minimum
P = Position
SAR = Stop And Reversal
t = current interval
X = length of current position
Y = AccelerationAdditionFactor value (used as initial AF and as the incremental value)
Z = AccelerationFactorLimit - the maximum value that the Acceleration Factor can reach
Interpretation
Before you can understand Wilder's calculations and methodology, some terms need additional explanation. The SAR is always the "stop and reverse" price point. This is the point you liquidate your current position and establish the opposite position.
The acceleration factor, a, is a weighting factor. In Wilder's work, the initial value for the acceleration factor is .02. The acceleration factor increases by a value of .02 each time the extreme price changes for the trade. You do not increment the acceleration factor if the extreme price fails to change. The value for a, acceleration factor, never exceeds .20 in Wilder's methodology.
The extreme price for the trade, EP, is just that. What was the highest or lowest price achieved during this trade? If you have a long position, use new highs as the extreme price. When you have a short position, use the new lows as the extreme price. The extreme price concept allows for normal market corrections without immediately triggering the SAR price, but it keeps the SAR price moving in the direction of the market. It allows the market to work in your favor for a brief time period, even though the market is correcting and the SAR price continues to converge with the price movement during this correction phase. Thus, the time/price factors are always at work within the parabolic study. Even if prices fail to move in your favor, the time factor continues to move the SAR toward current price levels.
Wilder has rules for the parabolic time/price study. They are:
First, a position is entered whenever prices penetrate the SAR. When this occurs, the new SAR becomes the extreme price from the previous trade. After the initial entry point, the applet calculates the SAR.
For the first day of entry, the SAR is the previous SIP (Significant Point). If long, the SIP is the lowest price reached while in the previous Short trade, If short, the SIP is the highest price reached while in the previous Long trade.
Next, the acceleration factor only increases when a new extreme price is set. When long, you only increment the acceleration factor when the market sets a new high, a new extreme price for the trade. Conversely, you increase the acceleration factor when new lows are made in a short position. If the extreme price does not change, you use the previous acceleration factor in the computations. Do not increase the acceleration factor. According to Wilder's rules and methods, the acceleration factor must not exceed .20 during the life of the trade.
Lastly, the new SAR price must not enter the trading range for the current or previous interval. In a long position, the new SAR must not exceed the low for current trading interval nor may it exceed the low for the previous trading interval. When short, the new SAR never falls below the high of the current or previous trading interval. If this condition occurs, you use either the lowest value of the two lows for a long position or the highest value of the two highs for a short position for the new SAR price.
Literature
Wilder, J. Welles. New Concepts in Technical Trading Systems. Greensboro, NC: Trend Research, 1978.
Le Beau C., Lucas D. W. Computer Analysis of the Futures Market. 1992.
Kaufman, Perry J. The New Commodity Trading System and Methods. 1987.